Textbook Question
Identify the type of transport (passive diffusion, facilitated transport, or active transport) that will occur for the following molecules:
(b) glucose, no energy required
1538
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
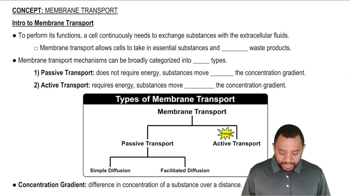


Identify the type of transport (passive diffusion, facilitated transport, or active transport) that will occur for the following molecules:
(b) glucose, no energy required
Identify the type of transport (passive diffusion, facilitated transport, or active transport) that will occur for the following molecules:
(b) nitrogen
Describe the concentration of the solution outside the cell as hypertonic or hypotonic if that solute is being transported across the cell membrane by
(b) facilitated transport.