Identify the type of transport described by each of the following:
a. A molecule moves through a protein channel.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: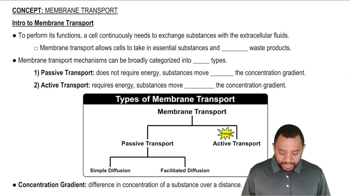



 1:21m
1:21mMaster Membrane Transport Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning