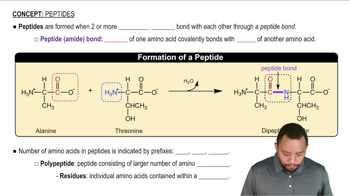
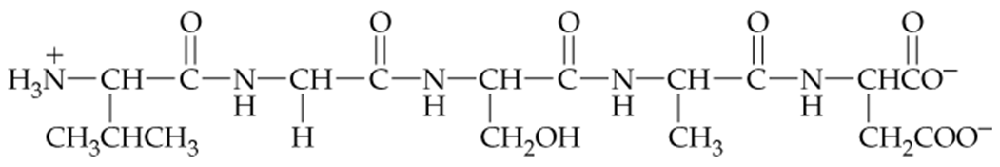
Aspartame, which is commonly known as NutraSweet™, contains the following dipeptide:
d. Draw the structure of the isomer of this dipeptide where the C-terminal and N-terminal amino acids are switched.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: