Textbook Question
Answer questions (a)–(e) concerning the following reaction:
b. Since hydrogens are removed, the enzyme belongs to what subclass of the enzyme class from part (a)?
1048
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

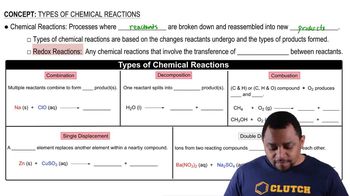

 :39m
:39mMaster Common Naming Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning