Textbook Question
Calculate the [H3O+] of each aqueous solution with the following [OH-]:
d. bile, 2.5 × 10-6 M
917
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: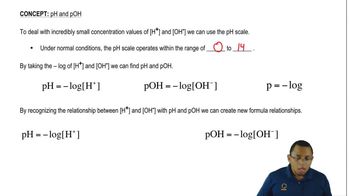



 1:31m
1:31mMaster The pH Scale Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning