Textbook Question
If a base is added to pure water, why does the [H3O+] decrease?
1199
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: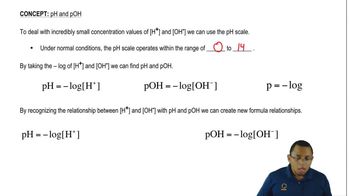



 1:31m
1:31mMaster The pH Scale Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning