Textbook Question
Identify all of the functional groups in each of the following molecules:
(b)
789
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
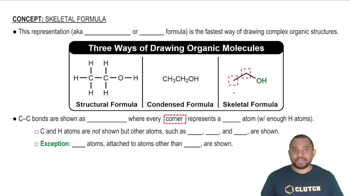


Identify all of the functional groups in each of the following molecules:
(b)
Name the four functional groups circled in the following molecule:
Write the condensed formula for each of the following molecules:
(b) 1,3-dichloro-3-methylheptane
Draw skeletal structures for each of the following molecules:
(b) cis-1-chloro-3-methylcyclohexane
A widely used general anesthetic is called halothane or Fluothane. Its IUPAC name is 2-bromo-2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane. Draw the Lewis structure for this compound.
The refrigerant 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane has been used in air conditioners in cars since the mid-1990s, but is being phased out due to its environmental impact. Draw the skeletal structure for this compound.