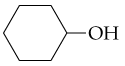
The following alkenes can be prepared by dehydration of an appropriate alcohol. Show the structure of the alcohol in each case that would provide the alkene shown as the major product.
b.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 1:3m
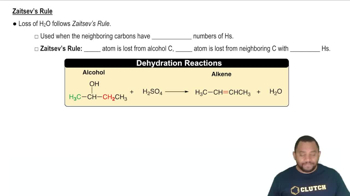
1:3mMaster Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning