Ch.14 Some Compounds with Oxygen, Sulfur, or a Halogen

Chapter 1, Problem 46b
The following alkenes can be prepared by dehydration of an appropriate alcohol. Show the structure of the alcohol in each case that would provide the alkene shown as the major product.
b. 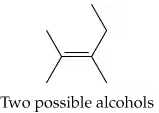
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the alkene structure provided in the problem. Note the position of the double bond and the number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
Recall that dehydration of an alcohol involves the removal of a water molecule (H₂O) to form an alkene. This reaction typically occurs in the presence of an acid catalyst, such as H₂SO₄, and heat.
Determine the alcohol that would lead to the given alkene as the major product. The hydroxyl group (-OH) in the alcohol must be located on a carbon adjacent to the carbon that will form the double bond. This is because the dehydration reaction follows the E1 or E2 elimination mechanism.
Apply Zaitsev's rule, which states that the major product of an elimination reaction is the more substituted alkene (the one with more alkyl groups attached to the double-bonded carbons). Use this rule to confirm the placement of the double bond in the alkene and identify the corresponding alcohol structure.
Draw the structure of the alcohol by replacing the double bond in the alkene with a single bond and adding a hydroxyl group (-OH) to one of the carbons involved in the double bond. Ensure the structure matches the requirements for the dehydration reaction to produce the given alkene as the major product.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Dehydration Reaction
A dehydration reaction is a chemical process where a water molecule is removed from a compound, typically resulting in the formation of a double bond. In organic chemistry, this often involves the conversion of alcohols to alkenes. Understanding this reaction is crucial for predicting the structure of the alcohol that can yield a specific alkene as the major product.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions Concept 1
Alcohol Structure
Alcohols are organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to a carbon atom. The structure of the alcohol influences the outcome of the dehydration reaction, including the stability of the resulting alkene. Recognizing the structural features of alcohols helps in determining which alcohol can be dehydrated to form a desired alkene.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Alcohol Classification Concept 2
Zaitsev's Rule
Zaitsev's Rule states that in elimination reactions, the more substituted alkene is typically the major product. This principle is important when predicting the outcome of dehydration reactions, as it guides the selection of the appropriate alcohol. By applying Zaitsev's Rule, one can deduce which alcohol will lead to the most stable alkene product after dehydration.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Zaitsev’s Rule Concept 2
0
