Oxytocin is a small peptide hormone involved in the process of birthing and lactation. It contains the nine amino acids shown.
CYIQNCPLG
a. How many nucleotides would be found in the mRNA for this protein?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: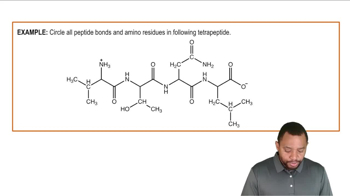


 2:42m
2:42mMaster Translation: Protein Synthesis Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning