The endorphins are a group of naturally occurring neurotransmitters that act in a manner similar to morphine to control pain. Research has shown that the biologically active parts of the endorphin molecules are simple pentapeptides called enkephalins. Draw the structure of the methionine enkephalin with the sequence Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Met. Identify the N-terminal and C-terminal amino acids.
Ch.18 Amino Acids and Proteins

Chapter 18, Problem 67
What is the sequence of atoms along the "backbone" of a protein?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that the 'backbone' of a protein refers to the repeating sequence of atoms that form the main structural framework of the protein, excluding the side chains (R groups).
Recall that proteins are polymers made up of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Each amino acid consists of an amine group (-NH₂), a carboxyl group (-COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain (R group) attached to a central carbon atom (the alpha carbon).
When amino acids link together to form a protein, the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amine group of another, forming a peptide bond and releasing a molecule of water (a condensation reaction).
The resulting backbone of the protein consists of a repeating sequence of atoms: -N-C-C-. Specifically, this sequence includes the nitrogen atom from the amine group, the alpha carbon atom, and the carbon atom from the carboxyl group of each amino acid.
This -N-C-C- sequence repeats throughout the length of the protein, forming the structural backbone, while the side chains (R groups) extend outward from the alpha carbon atoms, giving the protein its unique properties and functions.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Protein Structure
Proteins are complex molecules made up of amino acids, which are linked together in a specific sequence. The structure of a protein is crucial for its function, and it typically consists of four levels: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. The primary structure refers to the linear sequence of amino acids that form the protein's backbone.
Recommended video:
Guided course
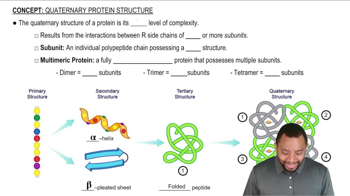
Quaternary Protein Structure Concept 1
Amino Acids
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, each containing an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a unique side chain. There are 20 standard amino acids, and their specific sequence determines the protein's structure and function. The backbone of a protein is formed by the peptide bonds between the amino acids, linking them in a chain.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Example 2
Peptide Bonds
Peptide bonds are covalent bonds that link amino acids together in a protein. They form through a dehydration reaction, where the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another, releasing a molecule of water. This bond creates the backbone of the protein, which is essential for maintaining its structural integrity and function.
Recommended video:
Guided course
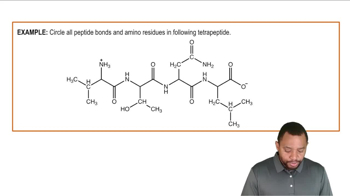
Peptides Example 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
357
views
Textbook Question
Identify the amino acids present in the peptide shown and name the peptide using the three-letter abbreviations.
306
views
Textbook Question
Identify the N-terminal and C-terminal amino acids of the peptide.
629
views
Textbook Question
Bradykinin, a peptide that helps to regulate blood pressure, has the primary structure Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg.
a. Draw the complete structural formula of bradykinin.
990
views
Textbook Question
Bradykinin, a peptide that helps to regulate blood pressure, has the primary structure Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg.
b. Bradykinin has a very kinked secondary structure. Why?
945
views
Textbook Question
Give an example of a protein containing primarily alpha-helices. Is this a fibrous or globular protein?
409
views
