Textbook Question
Fill in the following table comparing structural similarities between proteins and nucleic acids:
791
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

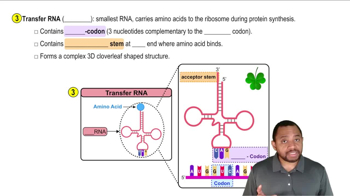

Fill in the following table comparing structural similarities between proteins and nucleic acids:
Write the complementary base sequence for each of the following DNA segments. Indicate the 5' and the 3' ends.
b. 5'ATAGCCCTTACTGG3'
Match the following statements with mRNA, rRNA, or tRNA:
a. combines with proteins to form ribosomes
List the possible codons for each of the following amino acids:
a. threonine
List the possible codons for each of the following amino acids:
a. valine
List the possible codons for each of the following amino acids:
c. histidine