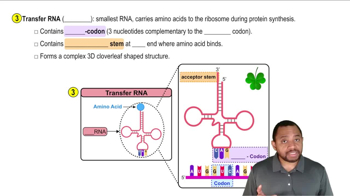
Textbook Question
What is the anticodon on tRNA for each of the following codons in an mRNA?
a. AGC
1444
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 2:43m
2:43mMaster Types of RNA Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning