Textbook Question
How many electrons are present in an atom in which the first and second shells and the 3s subshell are filled? Name the element.
1543
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
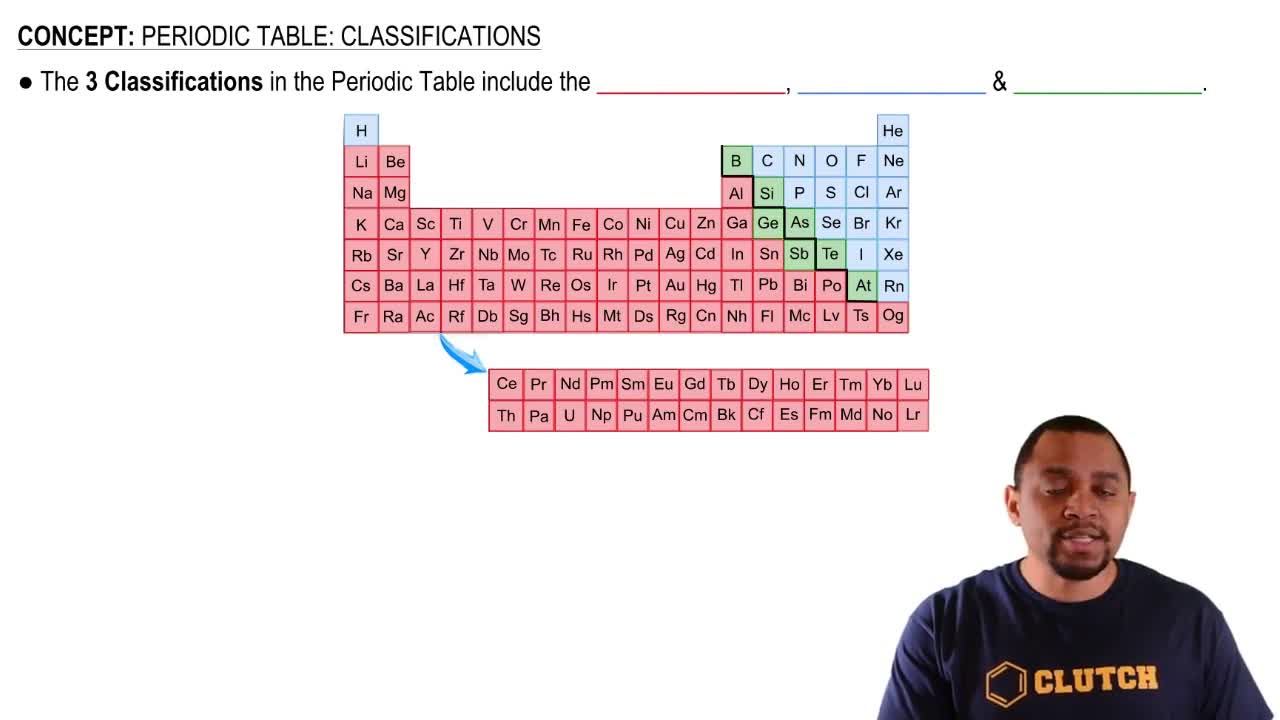


How many electrons are present in an atom in which the first and second shells and the 3s subshell are filled? Name the element.
An element has completely filled n = 1 and n = 2 shells and has six electrons in the n = 3 shell. Identify the element and its major group (i.e., main group, transition, etc.). Is it a metal or a nonmetal? Identify the orbital in which the last electron is found.
For chlorine, identify the group number, give the number of electrons in each occupied shell, and write its valence-shell configuration.