Textbook Question
Under what conditions might a reaction be endothermic but exergonic? Explain.
1757
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

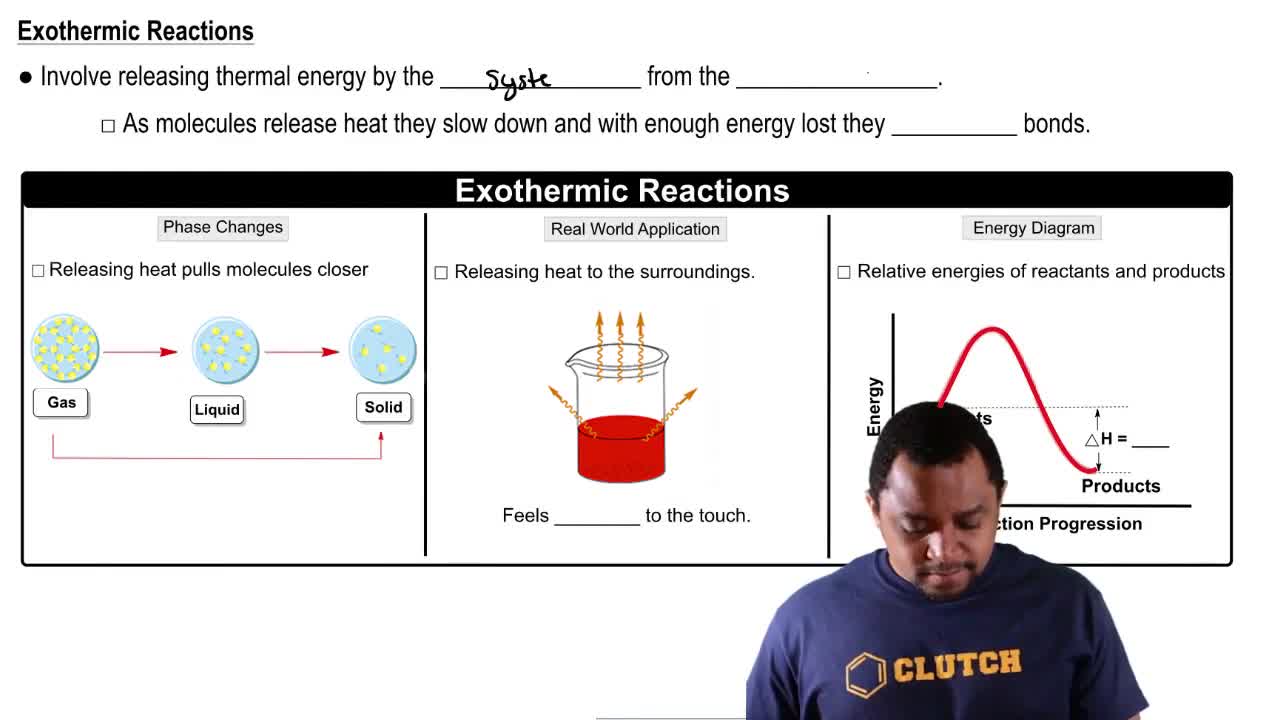

Under what conditions might a reaction be endothermic but exergonic? Explain.
For the reaction
b. Does entropy increase or decrease in this process?
For the reaction 2 Hg(l) + O2(g) → 2 HgO(s), ∆H = –43 kcal/mol (–180 kJ/mol).
a. Does entropy increase or decrease in this process? Explain.
The following reaction is used in the industrial synthesis of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) polymer:
Cl2(g) + H2C=CH2(g) → ClCH2CH2Cl(l) ∆H = –52 kcal/mol (–218 kJ/mol)
a. Is ∆S positive or negative for this process?
Which reaction is faster, one with Eact = +10 kcal/mol(+41.8 kJ/mol) or one with Eact = +5 kcal/mol(+20.9 kJ/mol)? Explain.
Why does increasing concentration generally increase the rate of a reaction?