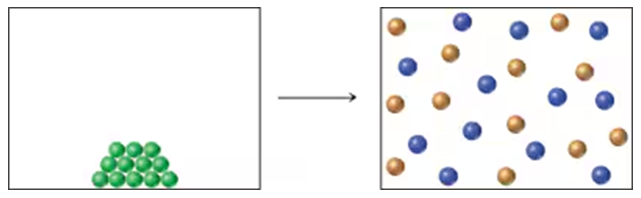
The change of state from liquid H2O to gaseous H2O has ∆H = +9.72 kcal/mol(+40.7 kJ/mol) and ∆S = -26.1 cal/(mol • K) [-109 J/(mol •K)].
a. Is the change from liquid to gaseous H2O favored or unfavored by ∆H? By ∆S?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 0:46m
0:46mMaster Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified) Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning