Textbook Question
Complete the following table for the three naturally occurring isotopes of silicon, the major component in computer chips:
1147
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
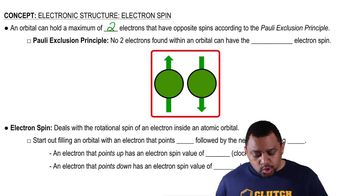


Complete the following table for the three naturally occurring isotopes of silicon, the major component in computer chips:
For each representation of a nucleus A through E, write the atomic symbol and identify which are isotopes.
a. <IMAGE>
Complete the following statements:
a. The atomic number gives the number of _____ in the nucleus.
Complete the following statements:
c. Sodium and potassium are examples of elements called _____.
Complete the following statements:
a. The number of protons and neutrons in an atom is also the _____ number.
Complete the following statements:
b. The elements in Group 7A (17) are called the _____.