Textbook Question
What are the two structural types of bases in DNA and RNA? Which bases correspond to each type?
744
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: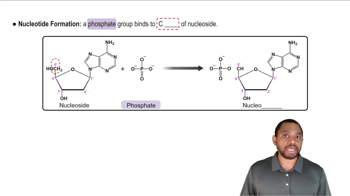



 1:49m
1:49mMaster Nitrogenous Bases Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning