Textbook Question
Draw structures for the following:
a. 2,4-Dinitrophenol
b. m-Ethylphenol
1022
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
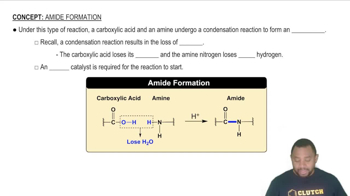
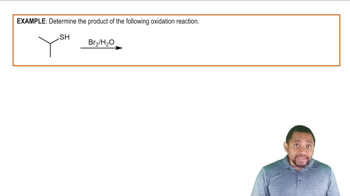

Draw structures for the following:
a. 2,4-Dinitrophenol
b. m-Ethylphenol
Name the following compounds:
a.
b.
Name the following compounds:
a.
b.
c.
Give systematic names for the following alkyl halides:
a.
b.
2-Aminopropane is an achiral molecule, but 2-aminobutane is chiral. Explain.
Which of the following molecules are chiral? (Hint: Draw each molecule and analyze it as illustrated in Worked Example 14.2.)
a. 3-Chloropentane
b. 2-Chloropentane
c.