Textbook Question
Indicate whether each of the following statements is characteristic of an acid, a base, or both
e. is an electrolyte
1074
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


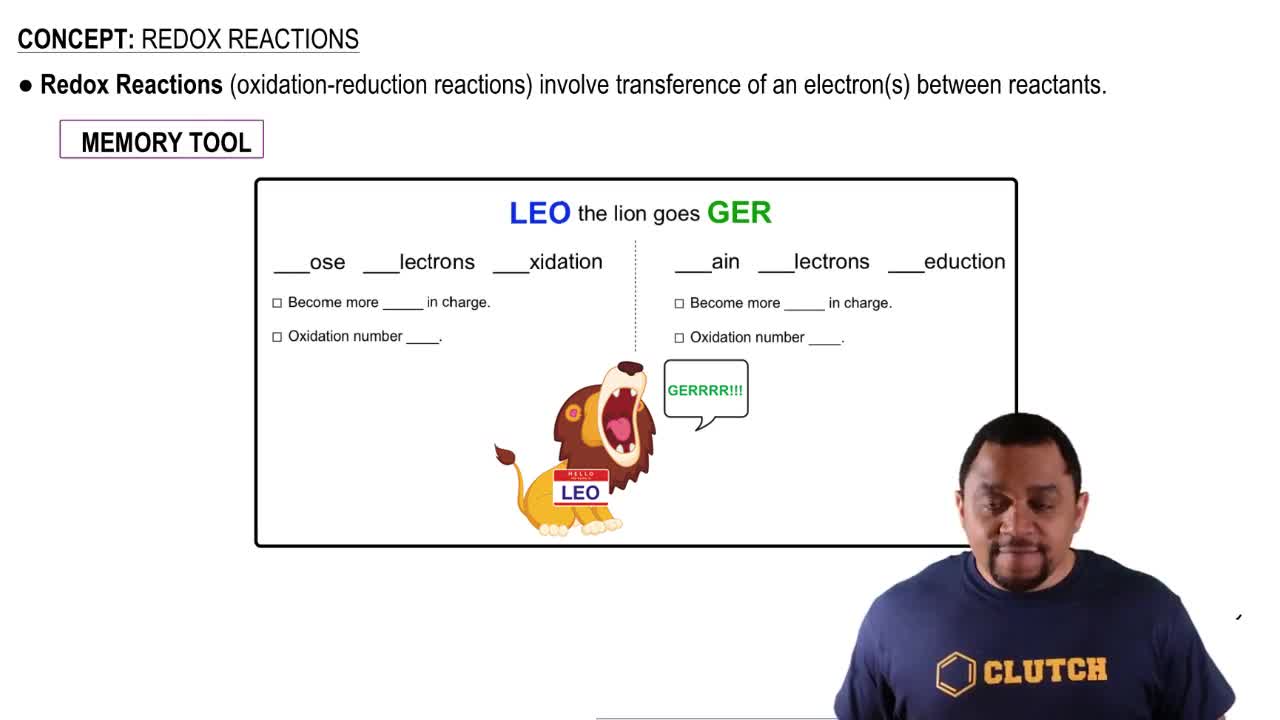
Indicate whether each of the following statements is characteristic of an acid, a base, or both
e. is an electrolyte
Indicate whether each of the following statements is characteristic of an acid, a base, or both:
a. neutralizes acids
Write formulas for each of the following acids and bases:
f. hypochlorous acid
Write the formula for the conjugate base for each of the following acids:
b. H2O
Write the formula for the conjugate base for each of the following acids:
a. HCO3-
Write the formula for the conjugate base for each of the following acids:
c. HPO42-