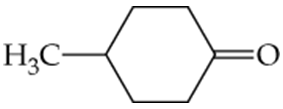
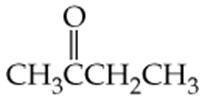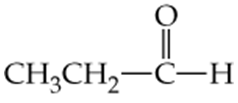Which of the following molecules contain aldehyde or ketone functional groups? You may want to refer to Table 15.1, Table 12.1, and Figure 15.3 to help in your identification. Copy the formulas and circle these functional groups.
a.
b.
c.
d. C4H9COCH3
e. C4H9CHO