Consider the following atoms in which X represents the chemical symbol of the element:
168X 169X 1810X 178X 188X
a. What atoms have the same number of protons?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Consider the following atoms in which X represents the chemical symbol of the element:
168X 169X 1810X 178X 188X
a. What atoms have the same number of protons?
Consider the following atoms in which X represents the chemical symbol of the element:
168X 169X 1810X 178X 188X
c. Which atoms have the same mass number?
Consider the following atoms in which X represents the chemical symbol of the element:
168X 169X 1810X 178X 188X
d. What atoms have the same number of neutrons?
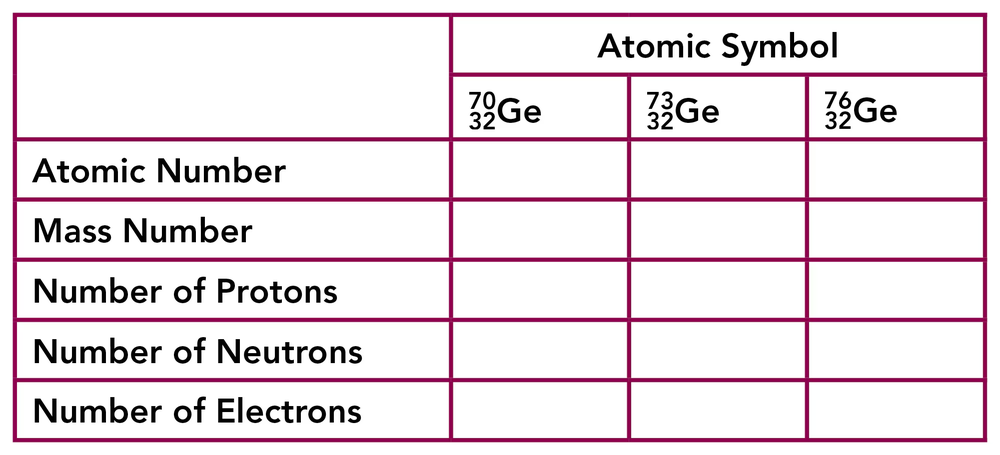
Complete the following table for the three naturally occurring isotopes of silicon, the major component in computer chips:
For each representation of a nucleus A through E, write the atomic symbol and identify which are isotopes.
a. <IMAGE>
Complete the following statements:
a. The atomic number gives the number of _____ in the nucleus.