Textbook Question
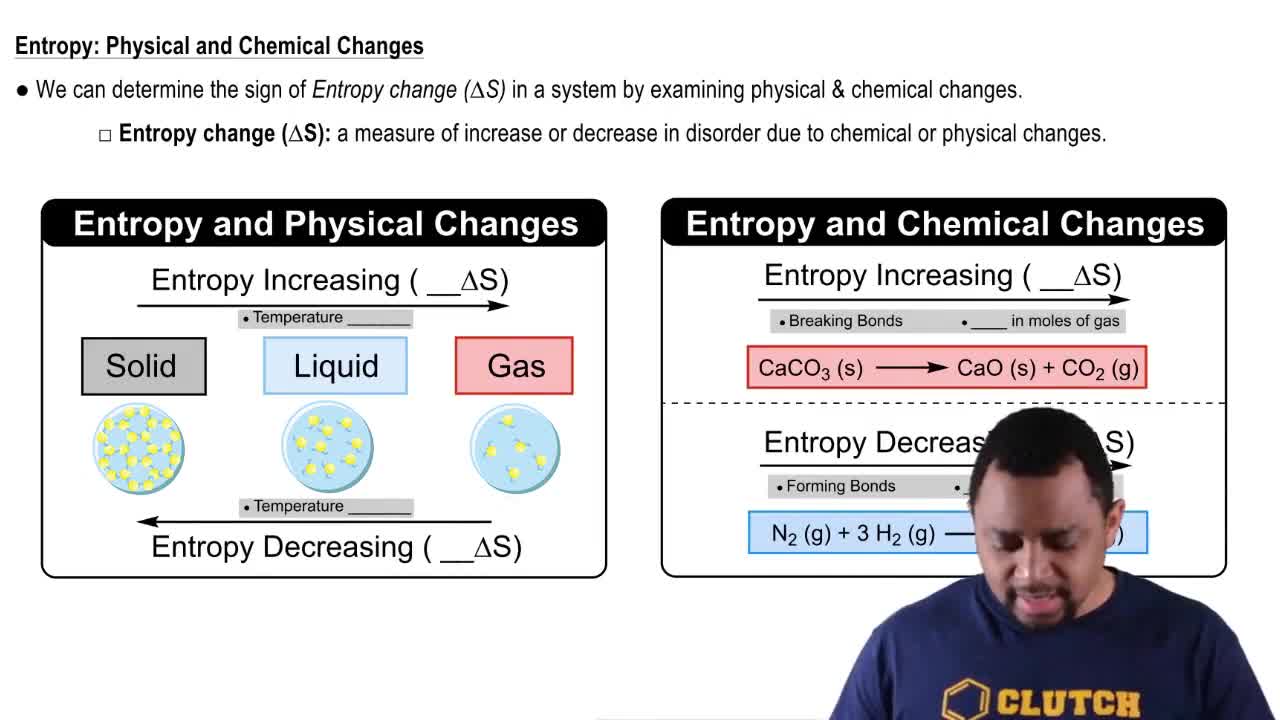
The change of state from liquid H2O to gaseous H2O has ∆H = +9.72 kcal/mol(+40.7 kJ/mol) and ∆S = -26.1 cal/(mol • K) [-109 J/(mol •K)].
a. Is the change from liquid to gaseous H2O favored or unfavored by ∆H? By ∆S?
1478
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

The change of state from liquid H2O to gaseous H2O has ∆H = +9.72 kcal/mol(+40.7 kJ/mol) and ∆S = -26.1 cal/(mol • K) [-109 J/(mol •K)].
a. Is the change from liquid to gaseous H2O favored or unfavored by ∆H? By ∆S?
Would you expect the boiling points to increase or decrease in the following series? Explain.
a. Kr, Ar, Ne
A local weather station reports the barometric pressure as 29.5 inHg (inches of Hg). Convert this pressure to torr and to atm.
Determine the percent composition of air in the lungs from the following composition in partial pressures: PN2= 573 mmHg, PO2 = 100 mmHg, PCO2 = 40 mmHg, and PH2O = 47 mmHg; all at 37 °C and 1 atm pressure.