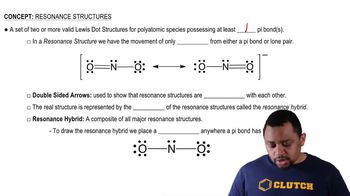
Textbook Question
Write structural formulas for compounds that meet the following descriptions:
a. An alkene, C6H12, that cannot have cis–trans isomers and whose longest chain is 5 carbons long
801
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Write structural formulas for compounds that meet the following descriptions:
a. An alkene, C6H12, that cannot have cis–trans isomers and whose longest chain is 5 carbons long
Write structural formulas for compounds that meet the following descriptions:
b. An alkene with a chemical formula of C10H12, that has cis–trans isomers and contains a benzene ring.
Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names:
a. trans-2-Pentene
b. trans-3,4-Dimethyl-3-hexene
c. 2-Methyl-1,3-butadiene
d. trans-3-Heptene
Draw and name all phenols with the formula C7H8O .
When ethylbenzene is reacted with nitric acid, three possible benzenes containing both a nitro group and an ethyl group are obtained. Draw and name them.