Textbook Question
What do the following abbreviations stand for?
c. NADH/H+
1535
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: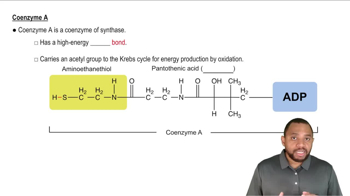



 2:23m
2:23mMaster Intro to Coenzymes Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning