Textbook Question
Write the name and symbol of the element with the following atomic number:
h. 92
1245
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance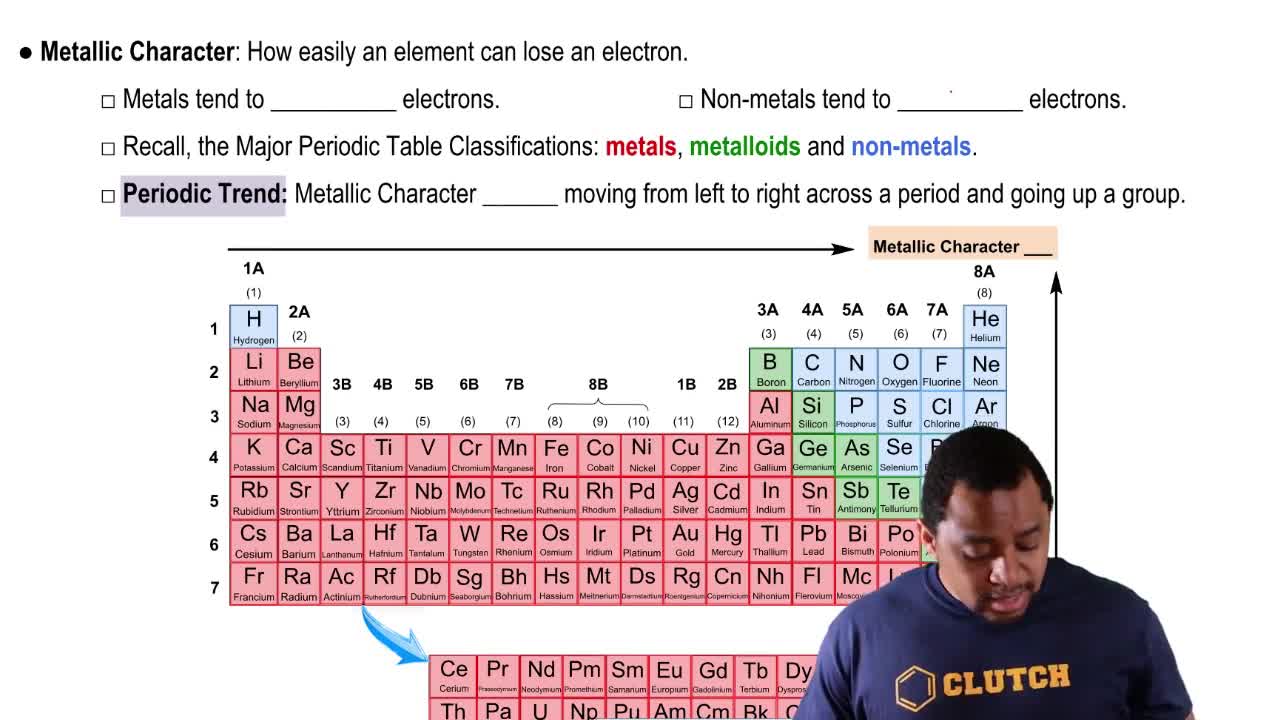
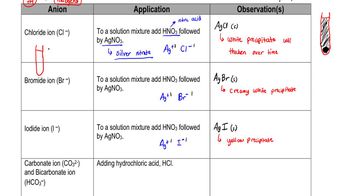
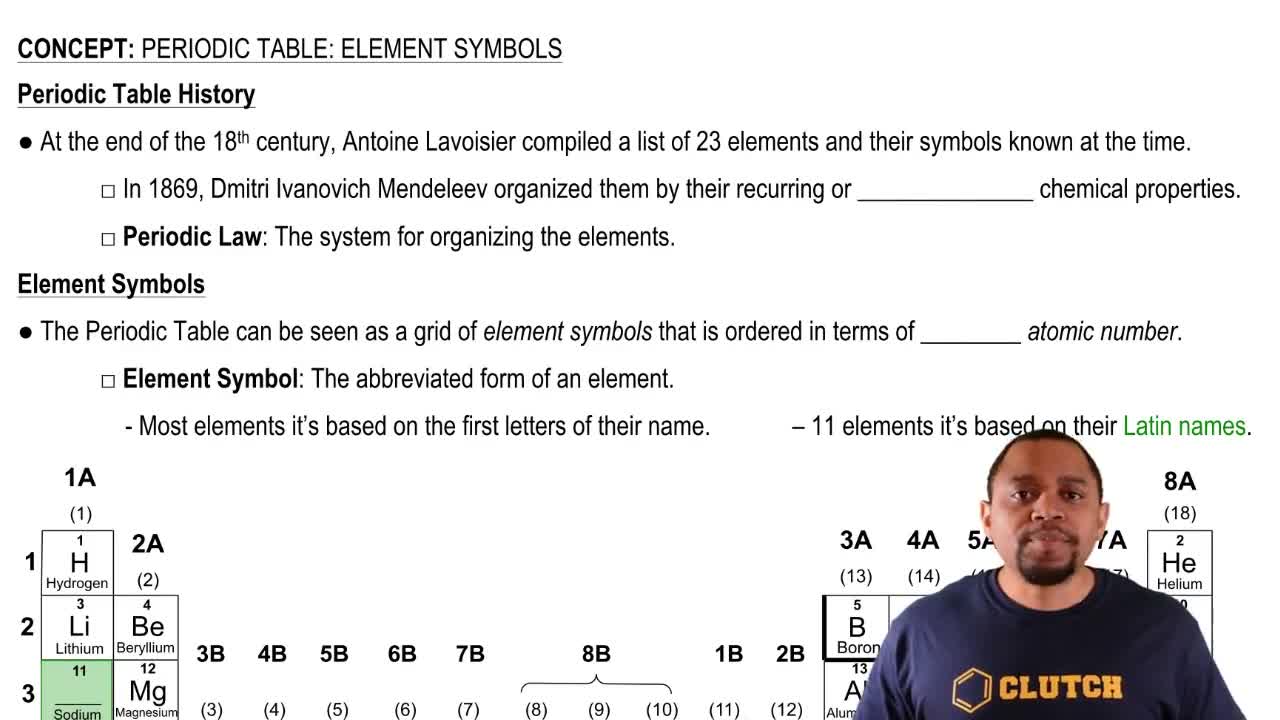
Write the name and symbol of the element with the following atomic number:
h. 92
Why is the ionization energy of Ca higher than K, but lower than that of Mg?
Why is the ionization energy of Cl lower than F, but higher than that of S?