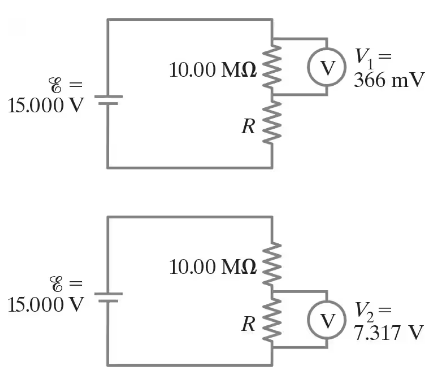
[In these Problems neglect the internal resistance of a battery unless the Problem refers to it.]
(II) A power supply has a fixed output voltage of 12.0 V, but you need VT = 3.0 V output for an experiment. (a) Using the voltage divider shown in Fig. 26–47, what should R₂ be if R₁ is 16.5 Ω? (b) What will the terminal voltage VT be if you connect a load to the 3.0-V output, assuming the load has a resistance of 7.0Ω?