[In these Problems neglect the internal resistance of a battery unless the Problem refers to it.]
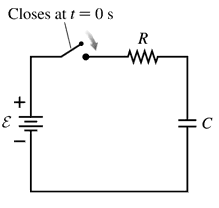
(II) What is the net resistance of the circuit connected to the battery in Fig. 26–46?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 17:24m
17:24mMaster Solving Resistor Circuits with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning