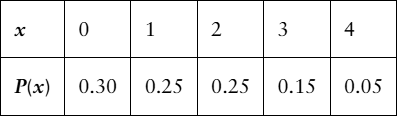
In Exercises 1–7, consider a grocery store that can process a total of four customers at its checkout counters each minute.
The mean increases to five arrivals per minute, but the store can still process only four per minute. Generate a list of 20 random numbers with a Poisson distribution for mu = 5 . Then create a table that shows the number of customers waiting at the end of 20 minutes.