Textbook Question
Find the area of each triangle ABC.
B = 124.5°, a = 30.4 cm, c = 28.4 cm
591
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: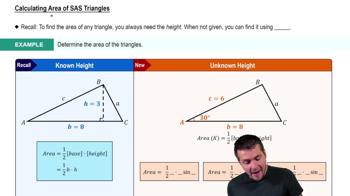



 4:27m
4:27mMaster Intro to Law of Sines with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning