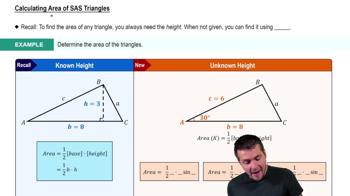
Find the area of each triangle using the formula 𝓐 = ½ bh, and then verify that the formula 𝓐 = ½ ab sin C gives the same result.
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:27m
4:27mMaster Intro to Law of Sines with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning