Gas exchange at the blood air barrier is efficient because
(a) The differences in partial pressure are substantial
(b) The gases are lipid soluble
(c) The total surface area is large
(d) Of all of these
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: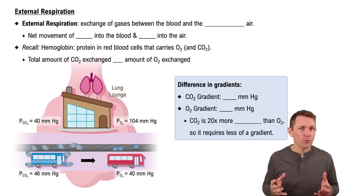



 6:12m
6:12mMaster Partial Pressure with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning