Multiple Choice
The complex of DNA and protein that makes up a eukaryotic chromosome is properly called __________.
2426
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
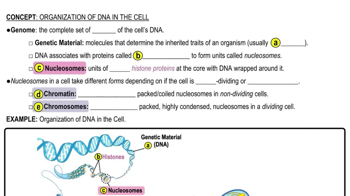


 6:51m
6:51mMaster Organization of DNA in the Cell with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning