The ions that enter the skeletal muscle cell during the generation of an action potential are
a. Calcium ions
b. Chloride ions
c. Sodium ions
d. Potassium ions
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
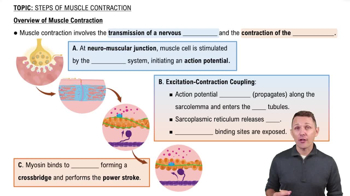
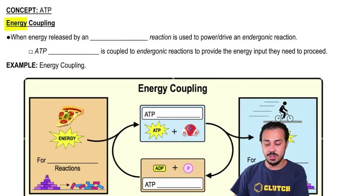
Verified video answer for a similar problem: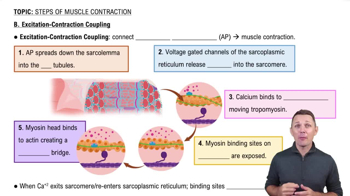

 4:53m
4:53mMaster Overview of Muscle Contraction with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning