a. Contrast unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar neurons structurally.
b. Indicate where each is most likely to be found.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: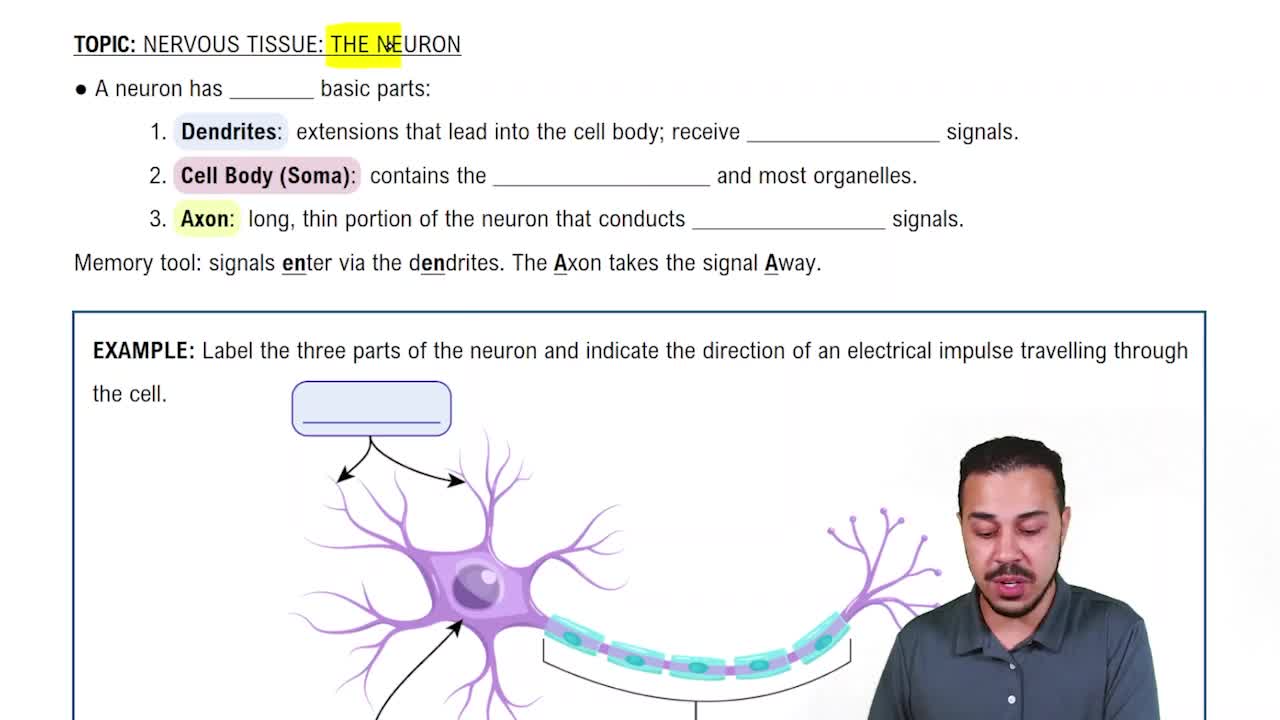


 1:32m
1:32mMaster The Central Nervous System with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning