There are several key concepts introduced in this chapter: Structure correlates with function; an animal's body has a hierarchy of organization with emergent properties at each level; and complex bodies have structural adaptations that increase surface area for exchange. Label the tissue layers shown in this section of the small intestine, and describe how this diagram illustrates these three concepts.

 Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition
Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition Ch. 20 Unifying Concepts of Animal Structure and Function
Ch. 20 Unifying Concepts of Animal Structure and Function Problem 5
Problem 5Briefly explain how the structure of each of these tissues is well suited to its function: stratified squamous epithelium in the skin, neurons in the brain, simple squamous epithelium lining the lung, bone in the skull.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
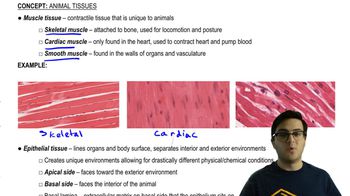
Neurons

Simple Squamous Epithelium
Which of the following body systems facilitates (but doesn't regulate) the functions of the other systems? respiratory system endocrine system digestive system circulatory system
Negative-feedback mechanisms are
a. Most often involved in maintaining homeostasis.
b. Analogous to a furnace that produces heat.
c. Found only in birds and mammals.
d. All of the above.
Which of the following best illustrates homeostasis? (Explain your answer.)
a. Most adult humans are between 5 and 6 feet tall.
b. All the cells of the body are about the same size.
c. When the salt concentration of the blood goes up, the kidneys expel more salt.
d. When oxygen in the blood decreases, you feel dizzy.
The diaphragm is a large sheet of muscle that helps move air in and out of your lungs. Breathing is automatically controlled by the brain, but you can choose to hold your breath or breathe deeper. What kind of muscle do you suppose makes up the diaphragm? (Explain your answer.)