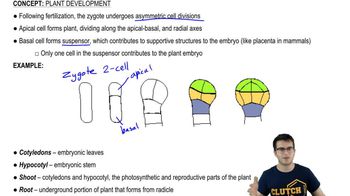
Complete the following concept map to test your knowledge of gene regulation.
<IMAGE>
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Complete the following concept map to test your knowledge of gene regulation.
<IMAGE>
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
Which of the following methods of gene regulation do eukaryotes and prokaryotes have in common?
a. Elaborate packing of DNA in chromosomes
b. Activator and repressor proteins, which attach to DNA
c. The addition of a cap and tail to mRNA after transcription
d. Lac and trp operons
A homeotic gene does which of the following?
a. It serves as the ultimate control for prokaryotic operons.
b. It regulates the expression of groups of other genes during development.
c. It represses the histone proteins in eukaryotic chromosomes.
d. It helps splice mRNA after transcription.
The control of gene expression is more complex in multicellular eukaryotes than in prokaryotes because __________. (Explain your answer.)
a. Eukaryotic cells are much smaller
b. In a multicellular eukaryote, different cells are specialized for different functions
c. Prokaryotes are restricted to stable environments
d. Eukaryotes have fewer genes, so each gene must do several jobs
Your bone cells, muscle cells, and skin cells look different because
a. Each cell contains different kinds of genes.
b. They are present in different organs.
c. Different genes are active in each kind of cell.
d. They contain different numbers of genes.
All your cells contain proto-oncogenes, which can change into cancer-causing oncogenes. Why do cells possess such potential time bombs?