23–68. Indefinite integrals Determine the following indefinite integrals. Check your work by differentiation.
∫ (csc² Θ + 2Θ² - 3Θ) dΘ
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: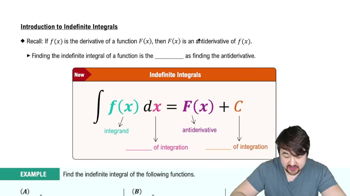



 5:04m
5:04mMaster Introduction to Indefinite Integrals with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning