The graph of a linear function f is shown. (a) Identify the slope, y-intercept, and x-intercept. (b) Write an equation that defines f.
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
2. Graphs of Equations
Lines
Problem 55
Textbook Question
For each line, (a) find the slope and (b) sketch the graph. 5x - 2y = 10
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Rewrite the given equation \$5x - 2y = 10\( in slope-intercept form \)y = mx + b\( by isolating \)y$ on one side.
Subtract \$5x\( from both sides to get \)-2y = -5x + 10$.
Divide every term by \(-2\) to solve for \(y\): \(y = \frac{-5x}{-2} + \frac{10}{-2}\).
Simplify the fractions to get \(y = \frac{5}{2}x - 5\), where the slope \(m = \frac{5}{2}\) and the y-intercept \(b = -5\).
To sketch the graph, plot the y-intercept \((0, -5)\) on the coordinate plane, then use the slope \(\frac{5}{2}\) to rise 5 units and run 2 units to find another point, and draw the line through these points.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
6mPlay a video:
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Slope of a Line
The slope measures the steepness and direction of a line, calculated as the ratio of the change in y to the change in x (rise over run). For a line in standard form Ax + By = C, the slope is found by rearranging to slope-intercept form y = mx + b, where m is the slope.
Recommended video:
Guided course

The Slope of a Line
Converting Standard Form to Slope-Intercept Form
To find the slope easily, rewrite the equation from standard form (Ax + By = C) to slope-intercept form (y = mx + b) by isolating y. This process involves solving for y, which reveals the slope (m) and y-intercept (b) directly.
Recommended video:
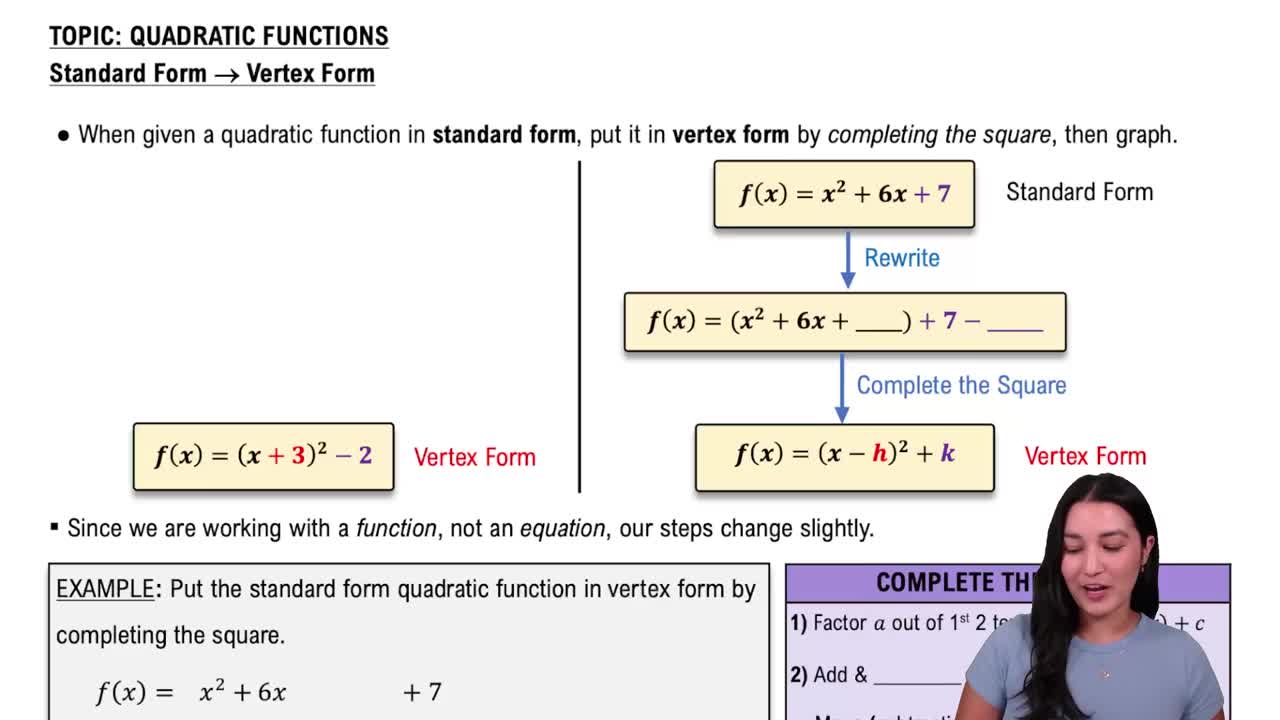
Converting Standard Form to Vertex Form
Graphing a Line Using Slope and Intercept
Graphing a line involves plotting the y-intercept on the coordinate plane and using the slope to find other points by moving vertically and horizontally. This method provides a visual representation of the line’s behavior and direction.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphing Lines in Slope-Intercept Form
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1933
views


