Textbook Question
Determine the pH of an HF solution of each concentration. In which cases can you not make the simplifying assumption that x is small? (Ka for HF is 6.8×10–4.) a. 0.250 M b. 0.0500 M c. 0.0250 M
2075
views
1
comments

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

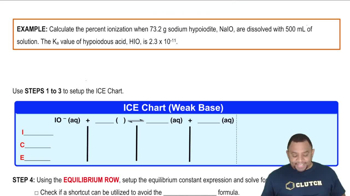

Determine the pH of an HF solution of each concentration. In which cases can you not make the simplifying assumption that x is small? (Ka for HF is 6.8×10–4.) a. 0.250 M b. 0.0500 M c. 0.0250 M
A 0.185 M solution of a weak acid (HA) has a pH of 2.95. Calculate the acid ionization constant (Ka) for the acid.
Determine the percent ionization of a 0.100 M HCN solution.
Calculate the percent ionization of a formic acid solution having the given concentration. a. 1.00 M
Calculate the percent ionization of a formic acid solution having the given concentration. b. 0.500 M