Which checkpoint is responsible for ensuring the DNA was replicated properly?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
9. Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis
Problem 1
Textbook Question
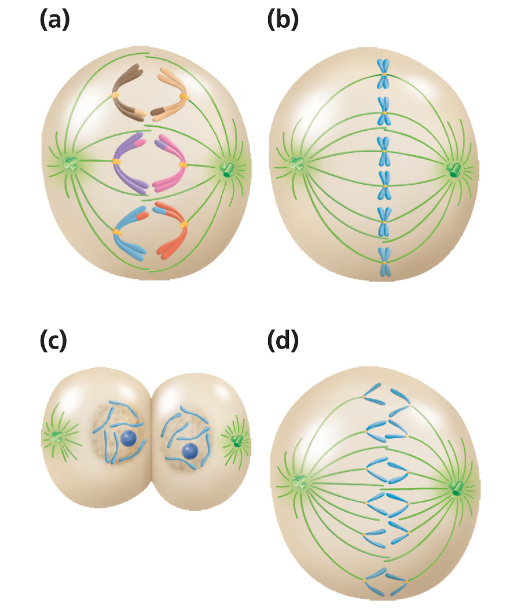
Examine the following diagrams of cells from an organism with diploid number 2n=6, and identify what stage of M phase is represented.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the diploid number 2n=6 means the organism has 6 chromosomes arranged in 3 homologous pairs. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids during M phase.
Step 2: Identify the key features of each stage of mitosis: (a) chromosomes aligned at the metaphase plate (metaphase), (b) chromosomes condensed but not yet aligned (prometaphase), (c) two daughter cells forming with separated chromosomes (telophase/cytokinesis), (d) chromosomes being pulled apart toward opposite poles (anaphase).
Step 3: Analyze image (a): chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell, attached to spindle fibers from opposite poles, indicating metaphase.
Step 4: Analyze image (b): chromosomes are condensed and spindle fibers are attached, but chromosomes are not yet aligned at the center, indicating prometaphase.
Step 5: Analyze image (c): two cells are forming with nuclei reappearing, indicating telophase and cytokinesis, and image (d): sister chromatids are being pulled apart toward opposite poles, indicating anaphase.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
58sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Stages of Mitosis
Mitosis is the process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells, consisting of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Each stage is characterized by specific chromosome arrangements and spindle fiber behaviors, which are critical for accurate chromosome segregation.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Mitosis Steps
Chromosome Behavior During Mitosis
During mitosis, chromosomes condense and become visible. In metaphase, chromosomes align at the cell's equatorial plate; in anaphase, sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles; in telophase, chromatids arrive at poles and begin to decondense, signaling the end of nuclear division.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mitosis Steps
Role of Spindle Fibers and Centrosomes
Spindle fibers, originating from centrosomes (microtubule organizing centers), attach to chromosomes at kinetochores and facilitate their movement. The organization and dynamics of spindle fibers are essential for proper chromosome alignment and segregation during mitosis.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chromosome Structure
Related Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
750
views
7
rank


