We usually think of enzymes as being most active at around 37°C, yet in PCR the DNA polymerase is subjected to multiple exposures of relatively high temperatures and seems to function appropriately at 65–75°C. What is special about the DNA polymerase typically used in PCR?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
18. Molecular Genetic Tools
Genetic Cloning
Problem 23
Textbook Question
You have generated three transgenic lines of maize that are resistant to the European corn borer, a significant pest in many regions of the world. The transgenic lines (T₁ in the accompanying table) were created using Agrobacterium-mediated transformation with a T-DNA having two genes, the first being a gene conferring resistance to the corn borer and the second being a gene conferring resistance to a herbicide that you used as a selectable marker to obtain your transgenic plants. You crossed each of the lines to a wild-type maize plant and also generated a T2 population by self-fertilization of the T1 plant. The following segregation results were observed (herbicide resistant : herbicide sensitive):
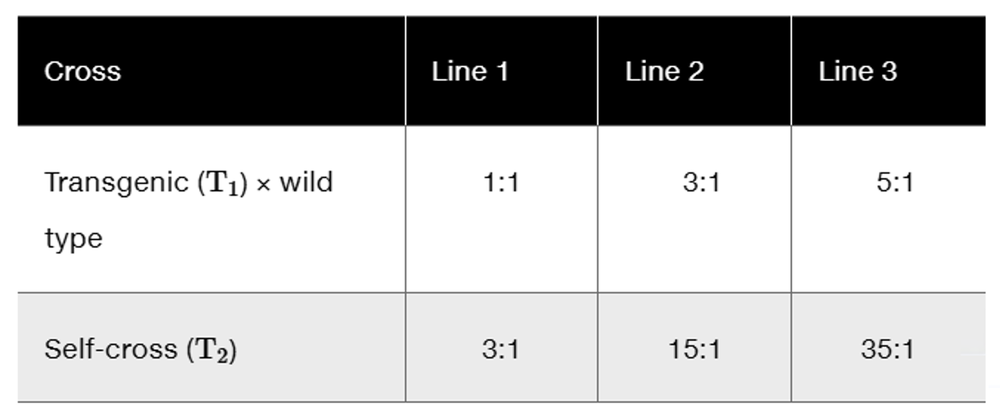
Explain these segregation ratios.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the genetic basis of the problem. The T-DNA contains two genes: one conferring resistance to the corn borer and another conferring resistance to a herbicide. The herbicide resistance gene is used as a selectable marker, and its segregation ratios provide insight into the inheritance patterns of the transgenic lines.
Step 2: Analyze the segregation ratios for the T₁ × wild type crosses. A 1:1 ratio in Line 1 suggests that the transgene is heterozygous and segregates in a Mendelian fashion. A 3:1 ratio in Line 2 indicates that the transgene is homozygous dominant. A 5:1 ratio in Line 3 suggests a more complex inheritance pattern, possibly involving multiple copies of the transgene or linked loci.
Step 3: Examine the segregation ratios for the T₂ self-crosses. A 3:1 ratio in Line 1 is consistent with Mendelian inheritance for a single heterozygous gene. A 15:1 ratio in Line 2 suggests the presence of two independent homozygous dominant loci. A 35:1 ratio in Line 3 indicates a higher number of loci or gene copies contributing to herbicide resistance.
Step 4: Relate the observed ratios to the genetic mechanisms. For Line 1, the 1:1 and 3:1 ratios suggest simple Mendelian inheritance of a single gene. For Line 2, the 3:1 and 15:1 ratios imply two independent loci or gene copies. For Line 3, the 5:1 and 35:1 ratios suggest a more complex genetic arrangement, such as multiple linked loci or tandem gene copies.
Step 5: Conclude that the differences in segregation ratios across the lines are due to variations in the genetic architecture of the transgenic insertions. Line 1 likely has a single copy of the transgene, Line 2 has two independent copies, and Line 3 has multiple linked copies or tandem repeats, leading to the observed ratios.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Transgenic Plants
Transgenic plants are genetically modified organisms that contain a gene or genes which have been artificially inserted instead of the plant acquiring them through reproduction. In this case, maize lines have been engineered to express genes for resistance to the European corn borer and a herbicide, allowing researchers to study the inheritance of these traits.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Plant Gamete Terminology
Segregation Ratios
Segregation ratios refer to the expected proportions of different phenotypes in the offspring of a genetic cross, based on Mendelian inheritance. The observed ratios, such as 1:1, 3:1, and 5:1, indicate how traits segregate during gamete formation and can reveal the number of alleles involved and their dominance relationships.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Organelle Inheritance
Selectable Markers
Selectable markers are genes introduced into transgenic organisms that confer a trait allowing for the identification of successfully modified individuals. In this scenario, the herbicide resistance gene serves as a selectable marker, enabling researchers to distinguish transgenic plants from non-transgenic ones during the selection process.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mapping with Markers
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
449
views


