Which of the following are sources of genetic variation during meiosis?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
9. Mitosis and Meiosis
Meiosis
Problem 2c
Textbook Question
Our closest primate relative, the chimpanzee, has a diploid number of 2n = 48. For each of the following stages of M phase, identify the number of chromosomes present in each cell.
End of meiotic anaphase II
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the diploid number of the chimpanzee: 2n = 48. This means the organism has 48 chromosomes in its diploid cells, with 24 chromosomes in each haploid cell (n = 24).
Recall that meiosis consists of two divisions: meiosis I and meiosis II. Meiosis II is similar to mitosis, where sister chromatids are separated into different cells.
At the end of meiotic anaphase II, sister chromatids have been pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell. Each chromatid is now considered an individual chromosome.
Since meiosis II starts with haploid cells (n = 24), and each chromosome splits into two chromatids during anaphase II, there will be 24 chromosomes at each pole of the cell.
After the completion of anaphase II, the cell will proceed to cytokinesis, resulting in two haploid daughter cells, each containing 24 chromosomes.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Diploid and Haploid Numbers
Diploid (2n) refers to cells that contain two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent. In the case of chimpanzees, the diploid number is 48, meaning they have 24 pairs of chromosomes. During meiosis, cells undergo two rounds of division, ultimately producing haploid (n) cells, which contain only one set of chromosomes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Diploid Genetics
Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized form of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in four genetically diverse haploid cells. It consists of two main stages: meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes are separated, and meiosis II, where sister chromatids are separated. Understanding the stages of meiosis is crucial for determining the chromosome number at specific points, such as anaphase II.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Meiosis Overview
Anaphase II
Anaphase II is a stage in meiosis II where the sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell. At this point, each chromatid is considered an individual chromosome. For chimpanzees, with a diploid number of 48, during anaphase II, there would be 48 chromosomes present in total, as each of the 24 pairs has been separated into individual chromatids.
Recommended video:
Guided course
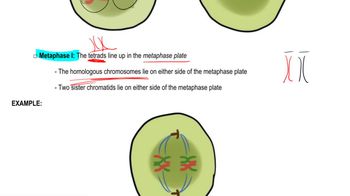
Meiosis Steps
Related Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
711
views
6
rank
2
comments


