Activation of which of the following genes leads to entrance into the lysogenic cycle?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
Lambda Bacteriophage and Life Cycle Regulation
Problem 13
Textbook Question
Describe the lytic and lysogenic life cycles of λ bacteriophage. What roles do λ repressor and Cro protein play in controlling transcription from PR and PRM, and how are these roles linked to lysis and lysogeny?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the two life cycles of λ bacteriophage: The lytic cycle involves the virus replicating and lysing the host cell to release new phages, while the lysogenic cycle integrates the phage DNA into the host genome, allowing it to replicate passively with the host cell without causing immediate harm.
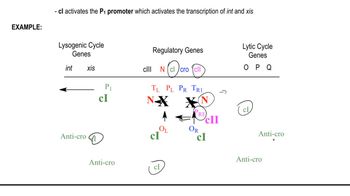
Explain the role of the λ repressor (also called CI protein): The λ repressor binds to the operator regions OL and OR, blocking transcription from the lytic promoters PL and PR. This repression ensures the virus enters and maintains the lysogenic cycle by preventing the expression of genes required for lysis.
Explain the role of the Cro protein: Cro protein binds to the same operator regions as the λ repressor but with different affinities. It represses transcription from PRM (the promoter for the λ repressor) and promotes transcription from PL and PR, favoring the lytic cycle by allowing the expression of lytic genes.
Describe the competition between λ repressor and Cro protein: The balance between these two proteins determines the life cycle. High levels of λ repressor maintain lysogeny by repressing lytic genes, while high levels of Cro protein shift the balance toward the lytic cycle by repressing the λ repressor and activating lytic genes.
Link the roles of PM and PRM to the life cycles: PM (maintenance promoter) is responsible for the continued expression of the λ repressor during lysogeny, while PRM (repressor maintenance promoter) is activated to produce more λ repressor. Cro protein inhibits PRM, tipping the balance toward lysis. This regulatory network ensures the phage can switch between cycles based on environmental conditions.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lytic and Lysogenic Life Cycles
The lytic cycle is a viral reproductive process where the virus infects a host cell, replicates its genetic material, and ultimately causes the cell to lyse, releasing new virions. In contrast, the lysogenic cycle involves the integration of the viral genome into the host's DNA, allowing it to replicate along with the host cell without causing immediate harm. This cycle can switch to the lytic phase under certain conditions, leading to cell lysis.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Decision Between Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles
λ Repressor and Cro Protein
The λ repressor is a protein that maintains the lysogenic state by binding to specific DNA sites, inhibiting the expression of genes necessary for the lytic cycle. Conversely, Cro protein promotes the lytic cycle by repressing the expression of the λ repressor. The balance between these two proteins determines whether the bacteriophage will enter the lytic or lysogenic cycle, influencing the fate of the host cell.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Proteins
Transcription Control from PM and PRM
PM and PRM are promoters that regulate the transcription of genes involved in the lytic and lysogenic cycles. PM drives the expression of genes necessary for the lytic cycle, while PRM is responsible for the maintenance of the lysogenic state by promoting λ repressor production. The interplay between these promoters, influenced by the levels of λ repressor and Cro protein, is crucial for determining whether the bacteriophage will undergo lysis or establish lysogeny.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Eukaryotic Transcription

 4:29m
4:29mWatch next
Master Bacteriophage Life Cycle with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
356
views
