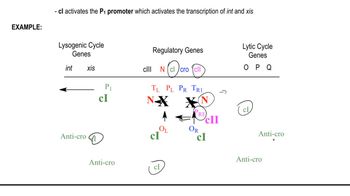
Describe the lytic and lysogenic life cycles of λ bacteriophage. What roles do λ repressor and Cro protein play in controlling transcription from PR and PRM, and how are these roles linked to lysis and lysogeny?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
Lambda Bacteriophage and Life Cycle Regulation
Problem 28f
Textbook Question
How would mutations that inactivate each of the following genes affect the determination of the lytic or lysogenic life cycle in mutated λ phage strains? Explain your answers.
N
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the role of the N gene in λ phage: The N gene encodes an antiterminator protein that allows RNA polymerase to bypass transcriptional terminators. This is essential for the expression of downstream genes required for both the lytic and lysogenic cycles.
Recognize the impact of an inactivated N gene: If the N gene is mutated and its protein is nonfunctional, transcription of downstream genes necessary for both the lytic and lysogenic pathways will be prematurely terminated. This would disrupt the phage's ability to proceed with either life cycle.
Analyze the effect on the lytic cycle: In the lytic cycle, the N protein is required to transcribe genes involved in DNA replication, structural proteins, and lysis. Without N, these genes cannot be expressed, and the lytic cycle cannot proceed.
Analyze the effect on the lysogenic cycle: In the lysogenic cycle, the N protein is also required to transcribe genes like cII, which is critical for the activation of the cI gene (encoding the λ repressor). Without N, the cI gene cannot be expressed, and the phage cannot establish lysogeny.
Conclude the overall effect: A mutation in the N gene would prevent the λ phage from successfully entering either the lytic or lysogenic life cycle, effectively rendering the phage nonfunctional in terms of its ability to propagate or integrate into the host genome.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles
The lytic and lysogenic cycles are two distinct pathways that bacteriophages, like λ phage, can follow after infecting a bacterial host. In the lytic cycle, the phage replicates rapidly, leading to the destruction of the host cell and the release of new phage particles. In contrast, the lysogenic cycle involves the integration of the phage DNA into the host genome, allowing it to replicate along with the host cell without causing immediate harm.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Decision Between Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles
Gene Function in Phage Life Cycles
Specific genes in λ phage are crucial for determining whether the phage enters the lytic or lysogenic cycle. For instance, genes that regulate the expression of proteins involved in the decision-making process, such as the cI repressor, play a significant role. Mutations that inactivate these genes can disrupt the balance between the two cycles, potentially favoring one pathway over the other.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Bacteriophage Life Cycle
Mutations and Their Effects
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can alter gene function. In the context of λ phage, mutations that inactivate genes essential for the lytic or lysogenic cycles can lead to a failure in the phage's ability to switch between these pathways. Understanding the specific roles of these genes helps predict how mutations will affect the phage's life cycle and its interaction with host bacteria.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Maternal Effect

 4:29m
4:29mWatch next
Master Bacteriophage Life Cycle with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
464
views
