Describe the difference between the bacteriophage lytic cycle and lysogenic cycle.
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
Lambda Bacteriophage and Life Cycle Regulation
Problem 27
Textbook Question
Two different mutations affect PRE. Mutant 1 decreases transcription from the promoter to 10% of normal. Mutant 2 increases transcription from the promoter to 10 times greater than the wild type. How will each mutation affect the determination of the lytic or lysogenic life cycle in mutant λ phage strains? Explain your answers.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the biological context: The λ phage can enter either the lytic or lysogenic life cycle. The decision is influenced by the levels of transcription of key genes, such as those encoding the CI repressor (favoring lysogeny) and Cro protein (favoring lysis). Transcription levels from the promoter are critical in determining which pathway is chosen.
Analyze the effect of Mutant 1: Mutant 1 decreases transcription from the promoter to 10% of normal. This means that the production of proteins encoded by this promoter will be significantly reduced. Consider how reduced transcription affects the balance between CI and Cro proteins, and whether it shifts the decision toward the lytic or lysogenic pathway.
Analyze the effect of Mutant 2: Mutant 2 increases transcription from the promoter to 10 times greater than the wild type. This results in a dramatic increase in the production of proteins encoded by this promoter. Evaluate how this overexpression impacts the balance between CI and Cro proteins, and whether it favors the lytic or lysogenic pathway.
Compare the two mutations: Contrast the effects of reduced transcription (Mutant 1) and increased transcription (Mutant 2) on the λ phage life cycle. Discuss how each mutation disrupts the normal regulatory mechanisms that control the decision between lysis and lysogeny.
Summarize the outcomes: Conclude how each mutation affects the determination of the lytic or lysogenic life cycle. Highlight the importance of precise transcriptional regulation in maintaining the balance between these two pathways in λ phage strains.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Transcription Regulation
Transcription regulation refers to the mechanisms that control the rate of gene expression by influencing the transcription of specific genes. In the context of phage λ, the ability of the promoter to initiate transcription is crucial for determining whether the phage enters a lytic or lysogenic cycle. Mutations that alter transcription levels can significantly impact the expression of genes responsible for these life cycles.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Eukaryotic Transcription
Lytic vs. Lysogenic Cycle
The lytic cycle is a viral reproductive process that results in the destruction of the host cell, while the lysogenic cycle allows the virus to integrate its genetic material into the host genome, remaining dormant. The decision between these two pathways is influenced by environmental conditions and the expression of specific genes, such as those controlled by the promoter affected by the mutations in the question.
Recommended video:
Guided course
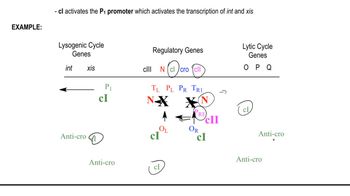
Decision Between Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles
Mutations and Their Effects
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can affect gene function and expression. In this scenario, Mutant 1 reduces transcription significantly, likely leading to a preference for the lysogenic cycle due to insufficient gene expression for lytic functions. Conversely, Mutant 2's increased transcription may push the phage towards the lytic cycle, as more lytic genes are expressed, promoting viral replication and cell lysis.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Maternal Effect

 4:29m
4:29mWatch next
Master Bacteriophage Life Cycle with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
333
views
