The human genome contains a large number of pseudogenes. How would you distinguish whether a particular sequence encodes a gene or a pseudogene? How do pseudogenes arise?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
16. Transposable Elements
Transposable Elements in Eukaryotes
Problem 22
Textbook Question
It is estimated that about 0.2 percent of human mutations are due to TE insertions, and a much higher degree of mutational damage is known to occur in some other organisms. In what way might a TE insertion contribute positively to evolution?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand what a Transposable Element (TE) is: TEs are DNA sequences that can change their position within the genome, sometimes creating or reversing mutations and altering the cell's genetic identity.
Recognize that while TE insertions can disrupt gene function and cause mutations, they can also introduce genetic variation, which is a raw material for evolution.
Consider how TE insertions might create new regulatory elements or modify existing ones, potentially leading to new patterns of gene expression that could be beneficial under certain environmental conditions.
Explore the possibility that TE insertions can facilitate exon shuffling or gene duplication events, which can generate novel genes or gene functions, contributing to evolutionary innovation.
Summarize that TE insertions contribute positively to evolution by increasing genetic diversity, enabling new gene functions, and providing raw material for natural selection to act upon.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Transposable Elements (TEs)
Transposable elements are DNA sequences that can move or copy themselves to new positions within the genome. They can disrupt gene function or regulation but also create genetic diversity by causing mutations, gene duplications, or rearrangements.
Recommended video:
Guided course
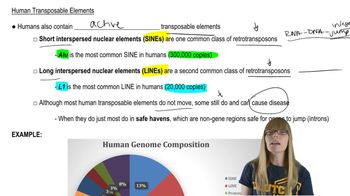
Human Transposable Elements
Mutations and Genetic Variation
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can be harmful, neutral, or beneficial. Genetic variation arising from mutations, including TE insertions, provides raw material for natural selection and evolutionary adaptation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Genomic Variation
Positive Evolutionary Impact of TE Insertions
TE insertions can contribute positively by creating new regulatory elements, altering gene expression, or generating novel genes. These changes can lead to advantageous traits that improve survival or reproduction, thus driving evolutionary innovation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Positional Cloning

 3:21m
3:21mWatch next
Master Eukaryotic Transposable Elements with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
532
views
