Compare the control of gene regulation in eukaryotes and bacteria at the level of initiation of transcription. How do the regulatory mechanisms work? What are the similarities and differences in these two types of organisms in terms of the specific components of the regulatory mechanisms?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
10. Transcription
Transcription in Eukaryotes
Problem 15
Textbook Question
Many promoter regions contain CAAT boxes containing consensus sequences CAAT or CCAAT approximately 70 to 80 bases upstream from the transcription start site. How might one determine the influence of CAAT boxes on the transcription rate of a given gene?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the role of CAAT boxes: CAAT boxes are regulatory elements in the promoter region of a gene that influence the binding of transcription factors and RNA polymerase, thereby affecting the transcription rate.
Design an experiment to mutate the CAAT box: Use site-directed mutagenesis to alter the CAAT or CCAAT sequence in the promoter region of the gene. This will help determine the effect of the CAAT box on transcription.
Create reporter gene constructs: Clone the wild-type promoter (with the intact CAAT box) and the mutated promoter (with the altered CAAT box) upstream of a reporter gene, such as luciferase or GFP, in separate plasmids.
Transfect cells with the constructs: Introduce the plasmids into a suitable cell line using a transfection method, such as electroporation or lipofection, to allow the cells to express the reporter gene under the control of the respective promoters.
Measure transcriptional activity: Quantify the reporter gene expression (e.g., by measuring luciferase activity or GFP fluorescence) for both the wild-type and mutated constructs. Compare the results to determine the influence of the CAAT box on transcription rate.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Promoter Regions
Promoter regions are specific DNA sequences located upstream of a gene that serve as binding sites for RNA polymerase and transcription factors. They play a crucial role in initiating transcription, as they determine when and how much of a gene is expressed. The presence of specific elements, such as CAAT boxes, can enhance the binding of transcription machinery, thereby influencing the transcription rate.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Regions of X Chromosomes
CAAT Boxes
CAAT boxes are conserved DNA sequences found in the promoter regions of many eukaryotic genes, typically located 70 to 80 base pairs upstream of the transcription start site. These sequences are recognized by transcription factors that enhance the efficiency of transcription initiation. The presence and integrity of CAAT boxes can significantly affect the transcriptional activity of associated genes, making them important for gene regulation.
Recommended video:
Guided course
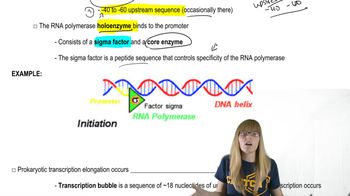
Prokaryotic Transcription
Transcription Rate
The transcription rate refers to the speed at which RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA from a DNA template during the transcription process. This rate can be influenced by various factors, including the presence of promoter elements like CAAT boxes, the availability of transcription factors, and the overall chromatin structure. Understanding how these elements interact helps in determining the expression levels of specific genes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Eukaryotic Transcription

 9:16m
9:16mWatch next
Master Eukaryotic Transcription with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
698
views
