Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Adaptor Hypothesis
The adaptor hypothesis, proposed by Francis Crick, suggests that tRNA acts as an adaptor molecule that translates the nucleotide sequence of mRNA into the amino acid sequence of proteins. It 'adapts' the genetic code by matching specific codons on mRNA with their corresponding amino acids during protein synthesis.
Recommended video:
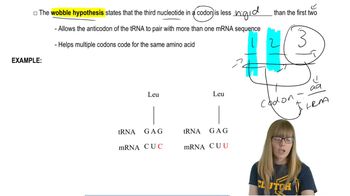
Translation:Wobble Hypothesis
Function of tRNA
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a small RNA molecule that carries amino acids to the ribosome during translation. Each tRNA has an anticodon region that pairs with a complementary mRNA codon, ensuring the correct amino acid is added to the growing polypeptide chain.
Recommended video:
Genetic Code Translation
The genetic code consists of codons, three-nucleotide sequences on mRNA that specify amino acids. Translation is the process where ribosomes read mRNA codons and, with the help of tRNA adaptors, assemble amino acids in the correct order to form proteins.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: