Draw the structures of the hemiacetals or hemiketals formed in these reactions:
b.

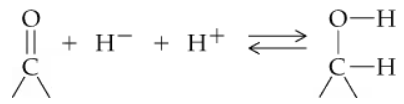
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Draw the structures of the hemiacetals or hemiketals formed in these reactions:
b.
For each compound shown next, determine whether it is a hemiacetal, a hemiketal, an acetal, or a ketal.
a.
b.
c.
d.
The carbonyl group can be reduced by addition of a hydride ion (H–) and (H+) a proton. Removal of H– and H+ from an alcohol results in a carbonyl group.
b. In the reaction, indicate which direction represents reduction and which represents oxidation.
A fundamental difference between aldehydes and ketones is that one can be oxidized to carboxylic acids but the other cannot. Which is which? Give an example of a test to differentiate aldehydes from ketones.
Glucose is the major sugar in mammalian blood. We often see it represented as either the "free aldehyde" or the cyclic hemiacetal forms shown here. Of the two forms of glucose, the cyclic hemiacetal is the preferred form found in blood. Can you suggest two reasons why?